By 2030, the number of adults affected by diabetes is projected to grow to 643 million in the U.S. alone, representing a nearly 20 percent increase from 2021. In addition to the vast number of individuals battling this chronic disease, an incredible amount of money is spent on diagnosing and managing diabetes. A total of 25 percent of all healthcare dollars in the U.S. are spent on caring for diabetes patients.
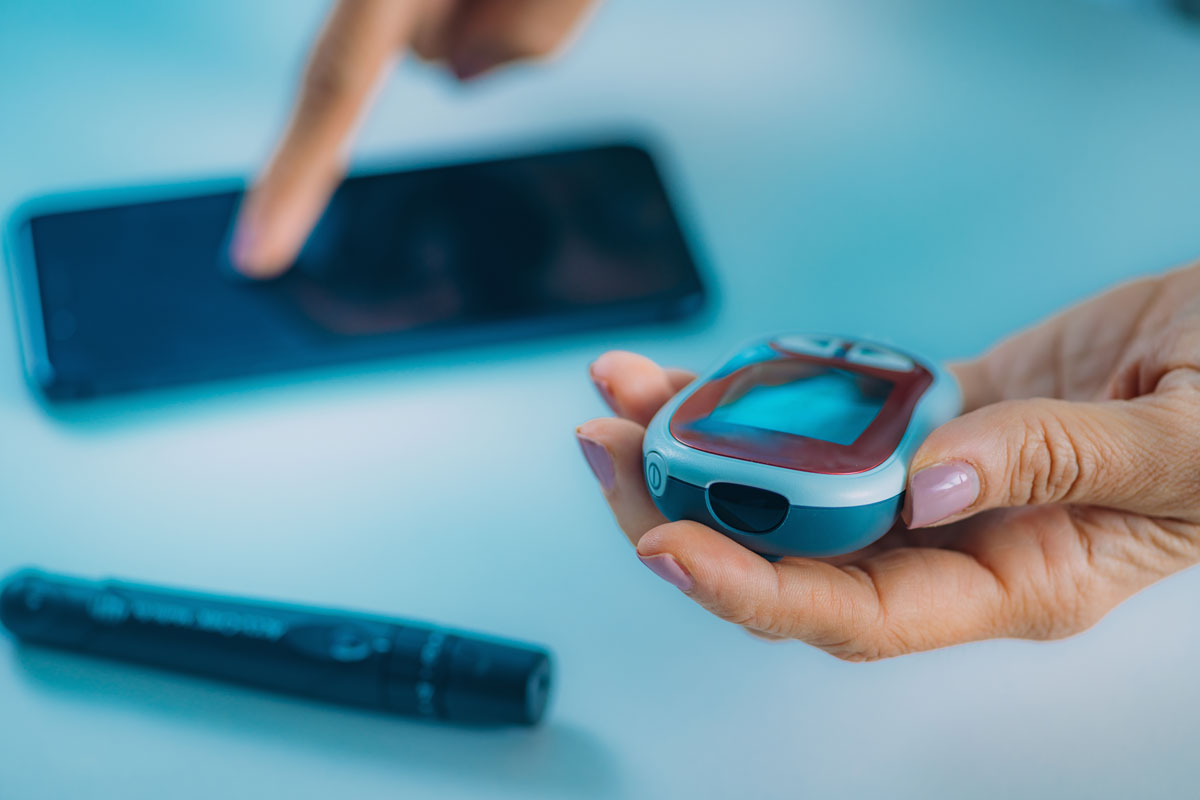
Historically, diabetes care management has been time intensive. Monitoring glucose levels required the use of a fingerstick glucose test. Patients had to check their blood sugar levels by pricking their fingers and placing their blood samples in a glucose meter. While this meter provided an accurate reading of the person’s blood sugar level at that time, this method could not capture fluctuations that may have occurred throughout the day. Additionally, these tests were inconvenient, requiring a person to stop what they were doing to perform the test.
The introduction of smart technology has changed everything. Through the use of smart wearables and artificial intelligence (AI), people with diabetes can more easily manage their condition and improve their health outcomes.
Smart technology is revolutionizing diabetes care in two key categories:
- Diagnostics
- Ongoing care
Smart Technology for Diabetes Diagnostics

Improved accuracy in blood sugar measurement is helping healthcare providers make more accurate diagnoses of diabetes. Through real-time test results, healthcare providers can determine whether a person has diabetes and which type. From here, correct diagnostic tools can help healthcare providers monitor the effectiveness of treatment for diabetes, and providers can measure whether a person’s treatment plan works and adjust accordingly.
The following are a few examples of how battery-powered edge devices are being put to work to help with diagnostics:
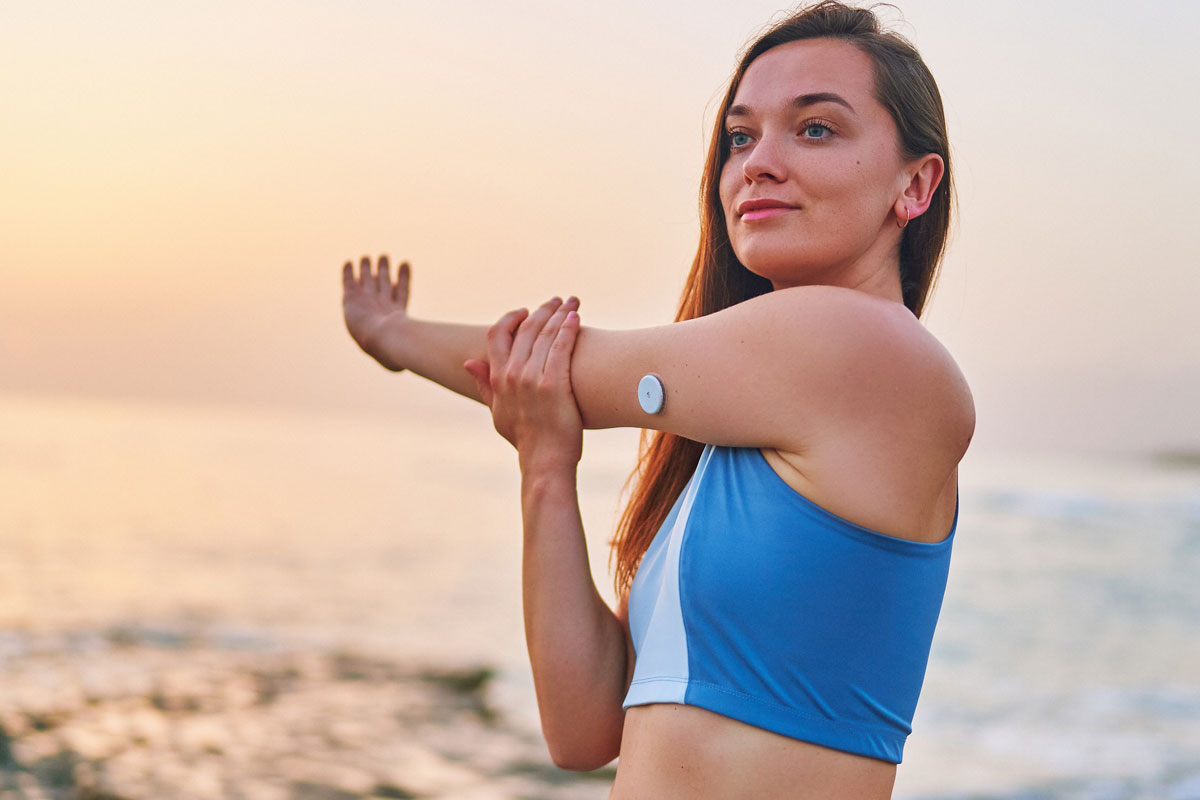
- Onalabs: Onalabs has developed connected devices that allow for the remote monitoring of glucose. These wearables work like fitness trackers, measuring glucose levels via sweat, eliminating the need for fingersticks, and enabling healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor the effectiveness of treatment from anywhere.
- Digital Diagnostics: Blood vessels in the retina can be damaged by high blood sugar levels. For this reason, patients with diabetes must have regular eye exams to detect any potential eye complications. Digital Diagnostics leverages AI to analyze retinal images, allowing healthcare providers to more accurately diagnose diabetic eye problems.
- Glyconics: Fingernails can provide healthcare providers with valuable information about a person’s health. Now, through a non-invasive handheld device, Glyconics is making it possible for healthcare providers to diagnose diabetes through changes in fingernail biomarkers.
Smart Technology for Diabetes Care Management
Beyond diagnostics, there are numerous ways that smart technology helps streamline diabetes care management. One of the key improvements is found in using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices. These smart devices use sensors to monitor blood sugar levels without requiring a finger prick, and CGM devices offer real-time data to the patient and their healthcare provider. This helps patients make better decisions about insulin dosing, diet, physical activity, and overall diabetes care management.
For example, the following devices simplify CGM:
- BeatO: Combining a non-invasive monitoring device and a smartphone app, BeatO provides diabetic patients with the ability to monitor blood glucose in real-time. Using an AI-powered chatbot, the app delivers assistance and reminders to patients.
- DiaMonTech and Vivalyf: These companies have developed devices that utilize fingerprints, optical scanning, and ultrasonic tagging sensors to provide continuous glucose monitoring non-invasively.
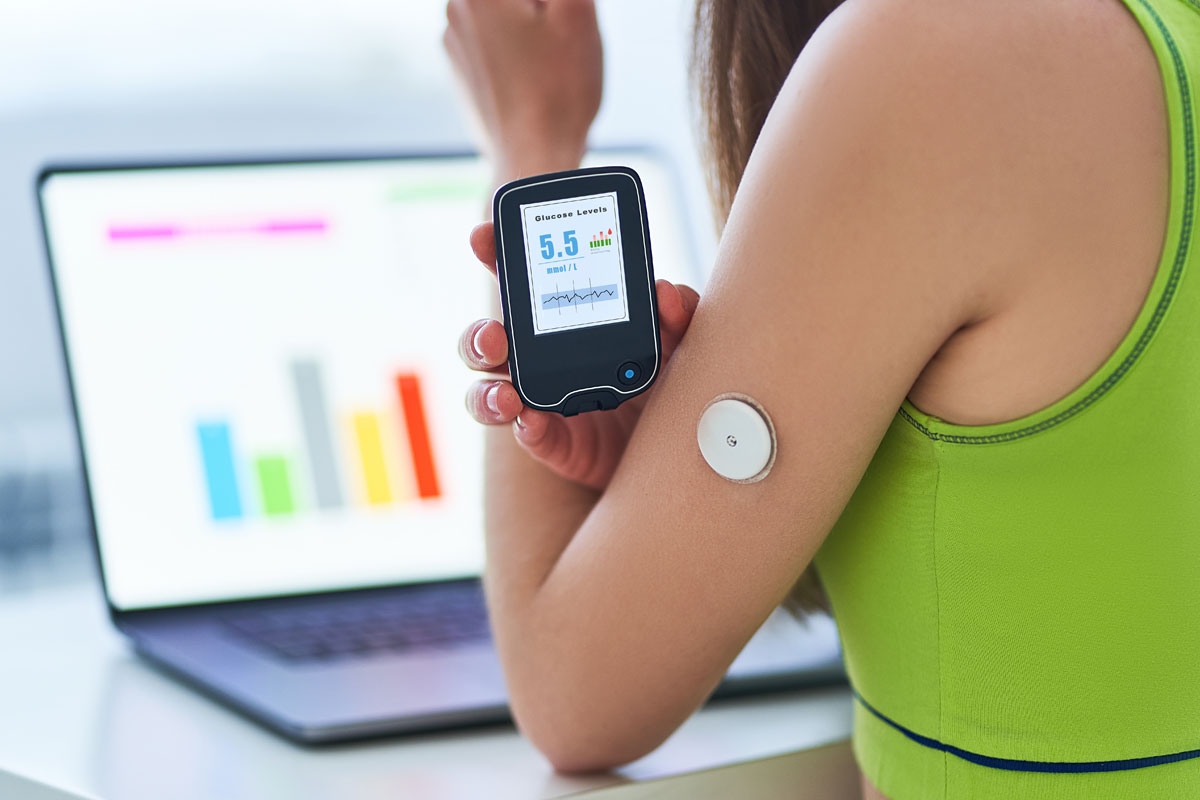
Along with monitoring glucose levels, those with diabetes must also deliver insulin to their bodies at the proper time. Smart technology is changing the game with insulin pumps and other smart devices that automatically deliver insulin to the body. What is advanced about these smart devices is how they adjust the amount of insulin delivered based on CGM readings.
- InPen: This reusable smart insulin pen sends dose information to a mobile app using Bluetooth technology. Through the smart pen, patients are provided with dose calculations and tracking.
- Glytec: Using advanced algorithms, Glytec helps healthcare providers analyze patient data and optimizes insulin dosing in hospital settings, simplifying the management of diabetes for both patients and healthcare providers.
- CeQur and ViCentra: These organizations have developed insulin solutions that supply medication on demand. These wearable devices offer a discreet method of insulin delivery paired with smart technology to make the management of glucose levels easier.
Along with these incredible tools, there are many apps and smart devices that are helping people with diabetes track blood sugar levels and medication use while also providing a more effective method of communication with their healthcare providers.
How Ambiq Contributes
For over a decade, Ambiq has been laser-focused on inventing and delivering the most revolutionary system-on-chip (SoC) solutions in the market. Ultra-low power SoCs from Ambiq® extends the processing capability and battery life in wireless devices and advanced wearables, enabling a more robust experience.
Through the advanced Sub-threshold Power Optimized Technology (SPOT®) platform, Ambiq has helped many leading manufacturers worldwide create products that can operate for days, months, and sometimes years on a lithium battery or a single charge. Visit https://ambiq.com/wearables for more information.