Thanks to the rise of edge devices like smartphones and the Internet of Things (IoT), our world has become much more connected. Whether it’s making our day-to-day lives more convenient with products connected to smart homes or powering smart industrial factories, edge devices enable the processing, transmitting, storing, and data. However, edge devices are also driving digital transformation in other vital industries, such as healthcare.
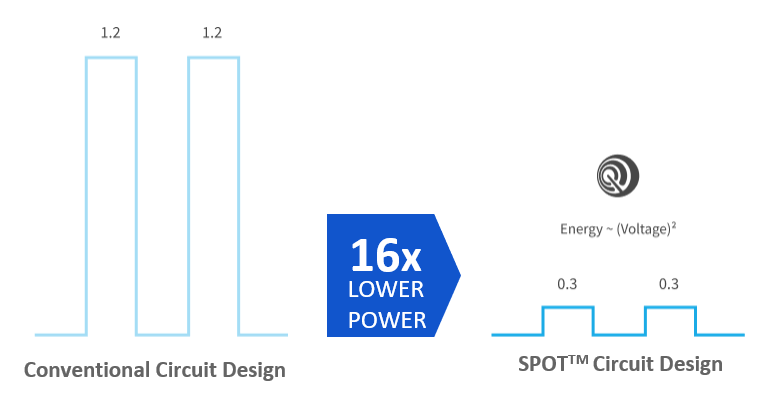
Ultra-low-power embedded solutions have managed to lower the power consumption by a factor of 16. When your IoT edge device can last up to weeks or even years without a battery recharge or replacement, many use cases become possible. This post will specifically focus on the impact of embedded devices on battery-powered edge devices in healthcare and examine the current use cases, benefits, and challenges.
Managing Edge Devices in Healthcare

Today, many healthcare organizations are already using many edge devices, such as blood pressure monitors, IV pumps, electrocardiogram and MRI machines, and implanted defibrillators. Other commonly found devices include printers, the imaging suite, biomedical devices, and IoT devices. The increase in the number of devices has made it more difficult for IT departments to manage.
As the number of devices grows, healthcare IT professionals must deal with two challenges in edge management. First is the issue of optimizing healthcare providers’ access to these lifesaving devices. The second is ensuring that these devices’ vital data are secured from harm. Unlike edge devices used in other industries like financial services, healthcare technologies are far less segmented. Different devices and applications need to communicate with each other to ensure excellent patient care. However, this also makes data security a more significant challenge.
Challenges
The number of networked medical devices and mobile edge devices across the healthcare industry is increasing, as is the amount of data being shared. More than ever, there is a great demand for real-time data to ensure that healthcare providers are making timely and accurate decisions for patient care. However, many healthcare organizations lack the IT resources to manage their network of edge devices effectively. These challenges include:
Security
Any time you have a network of connected devices transferring and sending data, there are bound to be questions of how to secure the data. Data security is especially important in healthcare, where sensitive patient data is sent between nurses, doctors, and surgeons regularly. However, according to a recent cybersecurity survey, only 22% of organizations did not experience a significant security incident in the previous 12 months. Security challenges are serious risks in the healthcare industry, and IT admins must be on the lookout for potential system vulnerabilities.

Device Management
Modern hospitals and healthcare organizations can have difficulty managing all of their edge devices. Often, their IT department has trouble securing (or even knowing) the devices on the network. For example, something as simple as a printer can cause headaches when configuring security control. As printers become more complex in their functionality and more versatile in processing power, IT staff must devote more resources to updating and securing these machines. Other devices like biomedical devices and imaging suites may be leased or purchased on contracts, making it more expensive and troublesome to handle.
Battery Life
Driven by new AI paradigms and new edge machine learning technologies, many edge devices are embedded with powerful processor chips. These processors enable cloud processing, or edge processing. However, this also places a higher strain on the device’s battery capabilities. Battery life and processing performance are looming in the background as the IT staff tends to other things. There might be hundreds of edge devices and medical equipment in a large hospital or healthcare organization, making it impractical to replace these devices’ batteries manually.
How Ambiq Is Helping
Whether it’s a blood pressure monitor or an IoT device, mission-critical edge devices need to be reliable in a healthcare setting. Especially for devices that rely on edge computing, a long-lasting battery life ensures that healthcare providers can spend more time with patients and less time troubleshooting tech problems.
At the heart of millions of edge devices is Ambiq’s ultra-low-power wireless SoCs that support vital technologies required by modern healthcare organizations such as Bluetooth Low Energy. Powered by Ambiq’s products, IoT devices can continue to evolve and help deliver the best patient care possible.