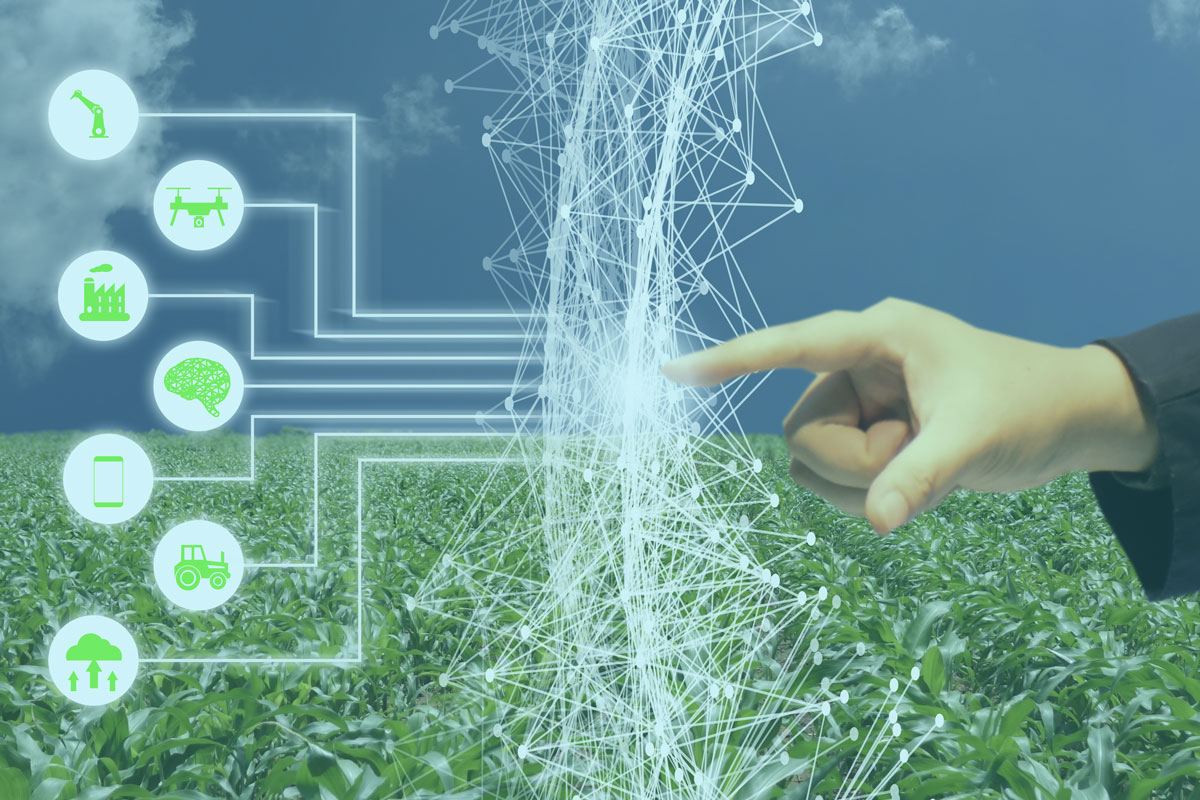
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) quickly come to mind when you think about consumer electronics, smart homes, electric vehicles, personalized shopping, and more. We see these advancements often on social media, in the news, and even use them daily. However, AI is also transforming the agriculture industry, a sector many consumers don’t interact with day-to-day. Modern-day agriculture exploded after World War I — 10.5% of the American workforce is employed in the agricultural sector, making it one of the most impactful industries for the economy and our food supply.
Now we’re in the midst of another evolution — AI solutions enable farmers to do more with less, improve quality, and ensure a faster go-to-market for crops. As the global population explodes to 8.5 billion by 2030, there is intense pressure on the agricultural industry to keep up with rising demand. AI stands poised to help the agriculture industry reduce food costs, improve crop yields, and work efficiently to feed billions of people. Here are a few different AI-driven technologies that are transforming the sector.
Machine-Learning Technology
Machine learning is when computer systems mimic intelligent human behavior and adapt and change based on inputs. Outcome prediction becomes more accurate as the machine learns more and more. In agriculture, ML technologies advance crop production in many ways. ML can analyze sensor data and historical trends to predict crop yields. It can help forecast the cost of production, make pesticide recommendations, and more. In pre-harvesting, machine learning can simplify crop breeding, which produces crops more resistant to volatile temperatures, droughts, and more. Machine learning can also identify plants, weeds, pests, and diseases and apply precision spraying to a hyper-targeted area with just the right amount of herbicide.
Cognitive Computing

Cognitive computing in agriculture can be used to learn, understand, and interact with different environments to boost productivity. In agriculture, cognitive computing can utilize prediction models to forecast agricultural challenges like droughts, weather, or pollution. Farmers can proactively protect crops, reduce loss, and maintain a greater harvest when they can prepare for these events.
IoT and Precision Farming
One of the most popular Internet of Things (IoT) applications is precision farming, which analyzes historical meteorology, soil reports, rainfall, and insect infestations. Techniques like site-specific crop management (SSCM) use automated seeders to ensure efficient production without over-depleting soil. AI sensors can also be used for precision farming, allowing farmers to hyper-target weeds and pests in specific zones versus spraying the entire field. This helps optimize the use of chemicals, water, and other resources. Precision farming can also be used for irrigation and fertilization, allowing for the perfect balance of resources to create the healthiest and largest amount of crops.
Drone Imagery
Drone photography is used for crop monitoring and field surveys, helping farmers increase yields and supplying them with real-time analytics and information. Drones can collect aerial data and use sensors for monitoring and assessment, delivering interactive reports to farmers. Farmers can quickly get info on problems like where the soil is depleted or areas with poor irrigation drainage causing flooding, allowing for increased soil, land, and other resource optimization.
Supply Chain Optimizations
The global supply chain is already an intensely strained process, and agriculture is no exception. However, delays in the agricultural supply chain can have disastrous effects. AI can be used to optimize the supply chain, helping improve logistics and transportation while reducing waste. AI can also consolidate systems, allowing for increased transparency and accessibility between vendors. Real-time monitoring and updates enable quick communication and problem-solving throughout the supply chain. AI can also bolster security; the agricultural supply chain is a highly sensitive, extremely interconnected system that can’t afford downtime due to a cyberattack.
How Ambiq Is Contributing
With all the AI and ML technologies being incorporated, the average farm is expected to generate 4.1 million data points every day by 2050. Over the next decades, climate change and global warming will accelerate while the economy goes through ups and downs — all as the world’s population rapidly increases. AI stands to touch everything in agriculture, from seed planting to harvesting to shipping food products to grocery stores, and these revolutionary techniques are already drastically transforming the industry, improving the lives of people around the world.
Ambiq® is uniquely committed to reducing the carbon footprint, creating edge intelligence and technology that offers more efficient use of energy. In agriculture, for example, Ambiq’s Apollo has been used in food smart labels for more efficient tracking, production, and transportation. Other Ambiq innovations are ready to support AI-enabled technologies in agriculture to increase the food supply, reduce the carbon footprint, support farmers, and bolster sustainability efforts.


